Understanding LSP with a Simple Emoji Completion Server
What is LSP?
Today I finally got around to checking out the Language Server Protocol (LSP). I’ve been curious about it for a while and wanted to see how it actually works under the hood.
LSP is basically just a standard way for text editors and language servers to talk to each other. These servers give you cool stuff like autocompletion, go-to-definition, and error checking. The awesome part? You write one server and it works with a bunch of different editors (VS Code, Neovim, Emacs, etc.) instead of having to build separate plugins for each one. Pretty neat, right?
Creating a Minimal LSP Server
To get the hang of LSP, I threw together a quick emoji autocomplete server in Go. Nothing fancy - it just does one job: suggests emojis when you type certain keywords.
Here’s the basic structure of my implementation:
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"github.com/tliron/commonlog"
"github.com/tliron/glsp"
protocol "github.com/tliron/glsp/protocol_3_16"
"github.com/tliron/glsp/server"
_ "github.com/tliron/commonlog/simple"
)
const lsName = "Emoji Autocomplete LS"
var (
version string = "0.0.1"
handler protocol.Handler
)
var emojiMapper = map[string]string{
"party": "🎉"
"bomb": "💣"
// ...other emoji mappings...
}
The core functionality consists of three main handlers:
- Initialize - Sets up the server and declares its capabilities
- Shutdown - Cleans up when the server is shutting down
- TextDocumentCompletion - Provides the actual completion items (emojis)
The completion handler is where the real work happens:
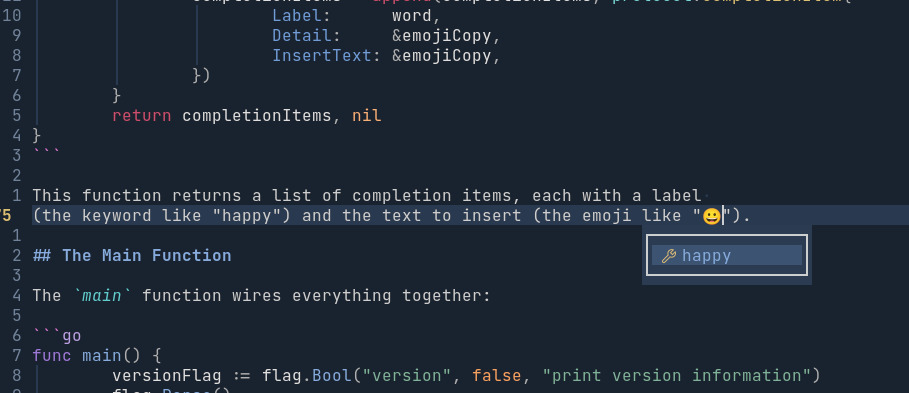
func textDocumentCompletion(context *glsp.Context, params *protocol.CompletionParams) (any, error) {
var completionItems []protocol.CompletionItem
for word, emoji := range emojiMapper {
emojiCopy := emoji
completionItems = append(completionItems, protocol.CompletionItem{
Label: word,
Detail: &emojiCopy,
InsertText: &emojiCopy,
})
}
return completionItems, nil
}
This function returns a list of completion items, each with a label (the keyword like “happy”) and the text to insert (the emoji like “😀”).
The Main Function
The main function wires everything together:
func main() {
versionFlag := flag.Bool("version", false, "print version information")
flag.Parse()
if *versionFlag {
printVersion()
return
}
commonlog.Configure(2, nil)
handler = protocol.Handler{
Initialize: initialize,
Shutdown: shutdown,
TextDocumentCompletion: textDocumentCompletion,
}
server := server.NewServer(&handler, lsName, true)
server.RunStdio()
}
This sets up the handler with our three functions and runs the server using standard input/output for communication.
Using the LSP Server in Neovim
After compiling the server, I could use it in Neovim with this simple configuration:
vim.lsp.start({
name = "my-lsp",
cmd = { "./my-lsp" },
root_dir = vim.fn.getcwd(),
})
and then source it:
source test.lua
What I Learned
Building this little LSP server taught me some cool stuff:
How LSP is Built - Now I get how the whole thing works. Your editor is the client, and it talks to the language server using a standard way of communicating.
Servers Tell What They Can Do - When a server starts up, it basically says “Hey, I can do completions, formatting, etc.” so the editor knows what to ask for.
Back-and-Forth Talking - The editor asks things like “what completions should I show here?” and the server answers back with the goods. It’s just sending JSON messages back and forth.
Start Small, Add More Later - You don’t have to build everything at once. I started with just completions, but I could add more cool features later.
Super Easy to Hook Up - Once your server is working, plugging it into different editors is way easier than I thought it would be.
Next Steps
This was just a super basic version, but it’s a good jumping-off point. Some stuff I might add later:
- Make the server keep track of what’s in the file as you type
- Add those little pop-ups when you hover over an emoji to show what it means
- Maybe throw in some error checking for custom stuff
- Add auto-formatting so things look nice
The cool part? When I add any of this stuff to my server, bam! It works in pretty much any editor that knows LSP - VS Code, Emacs, Neovim, whatever.
Helpful Stuff I Found
If you wanna learn more about LSP, check these out:
- Official LSP Docs - kinda dry, but good info
- GLSP Library for Go - this made my life way easier
- Neovim LSP Docs - for hooking everything up in Neovim